
Pure tone testing (audiogram) - For this test, you wear earphones attached to the audiometer. It is tapped and placed against the bone behind each ear (mastoid bone) to test bone conduction.Ī formal hearing testing can give a more exact measure of hearing. The tuning fork is tapped and held in the air on each side of the head to test the ability to hear by air conduction. These may include completing a questionnaire and listening to whispered voices, tuning forks, or tones from an ear examination scope.Ī specialized tuning fork test can help determine the type of hearing loss. Your health care provider may test your hearing with simple tests that can be done in the office. The normal range of human hearing is about 20 to 20,000 Hz. Shrill, high-pitched tones range around 10,000 Hz or higher. Low bass tones range around 50 to 60 Hz. The TONE of sound is measured in cycles per second (cps) or Hertz (Hz): Louder sounds can cause immediate pain, and hearing loss can develop in a very short time. Sounds greater than 85 dB can cause hearing loss after a few hours. Loud music (some concerts) is around 80 to 120 dB. The INTENSITY of sound is measured in decibels (dB): 
They can also pass through the bones around and behind the ear (bone conduction). Sound waves can travel to the inner ear through the ear canal, eardrum, and bones of the middle ear (air conduction).
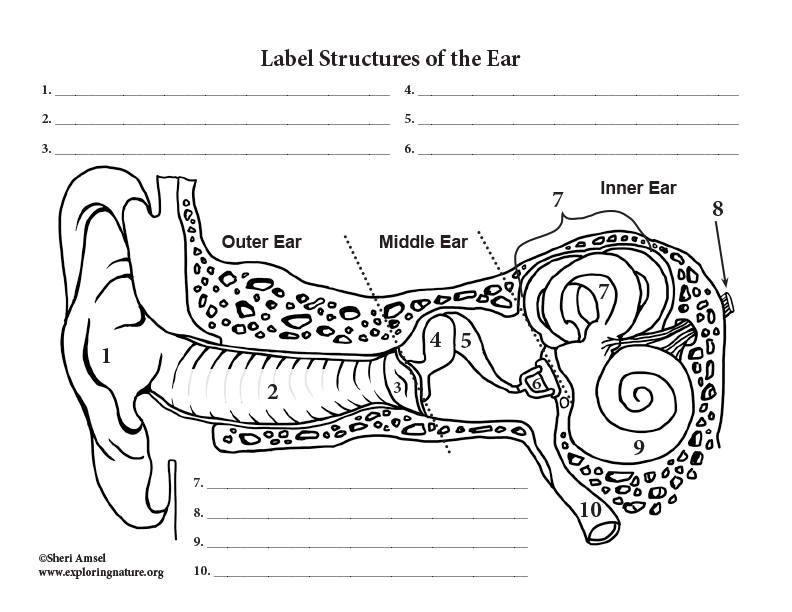
The sound then travels along nerve pathways to the brain. Hearing occurs when sound waves stimulate the nerves of the inner ear. Sounds vary, based on their loudness (intensity) and the speed of sound wave vibrations (tone).

An audiometry exam tests your ability to hear sounds.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
